OSINT in Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Investigations: Unmasking Financial Shadows


When the main characters in "Breaking Bad" made millions by selling banned substances, they couldn’t spend a penny without attracting unwanted attention. What was the solution to this problem? A money laundering scheme, of course. Ironically, this imaginary situation is not so different from real life. Modern criminals constantly search for new ways to outsmart investigators and legitimize their earnings while authorities strive to dispense justice.
In our new article, we will dive into the significance of anti-money laundering measures in combating financial fraud and crime. We will explore the current shortcomings and challenges AML efforts face and discover practical solutions that OSINT provides to track suspicious activities and break through the investigation barriers.
Let's get started!
Many people often confuse money laundering and anti-money laundering (AML). While these two terms are closely related, they address different aspects of the same issue. So, let's start with the basics and understand both definitions through real examples.
Money Laundering. Illegal activities, such as smuggling, bribery, and organized crime, generate large sums of illicit cash. However, malicious actors cannot spend these funds without raising suspicion from financial institutions. This is where money laundering comes into play. It is a process that makes illegally obtained funds appear legitimate.
Several methods are used for money laundering, but a common approach involves channeling unlawful currency into a legal business. Doing so makes the funds appear to be earned through authorized means. Typically such a scheme involves three stages: placement, layering, and integration. To understand it better, imagine a drug dealer who owns a car wash. The placement stage would be the criminal mixing the illegal cash into his business. Layering is when making it look like the company is very successful by creating phony invoices and sales. Finally, integration is the end result, the illusion of “clean” income.
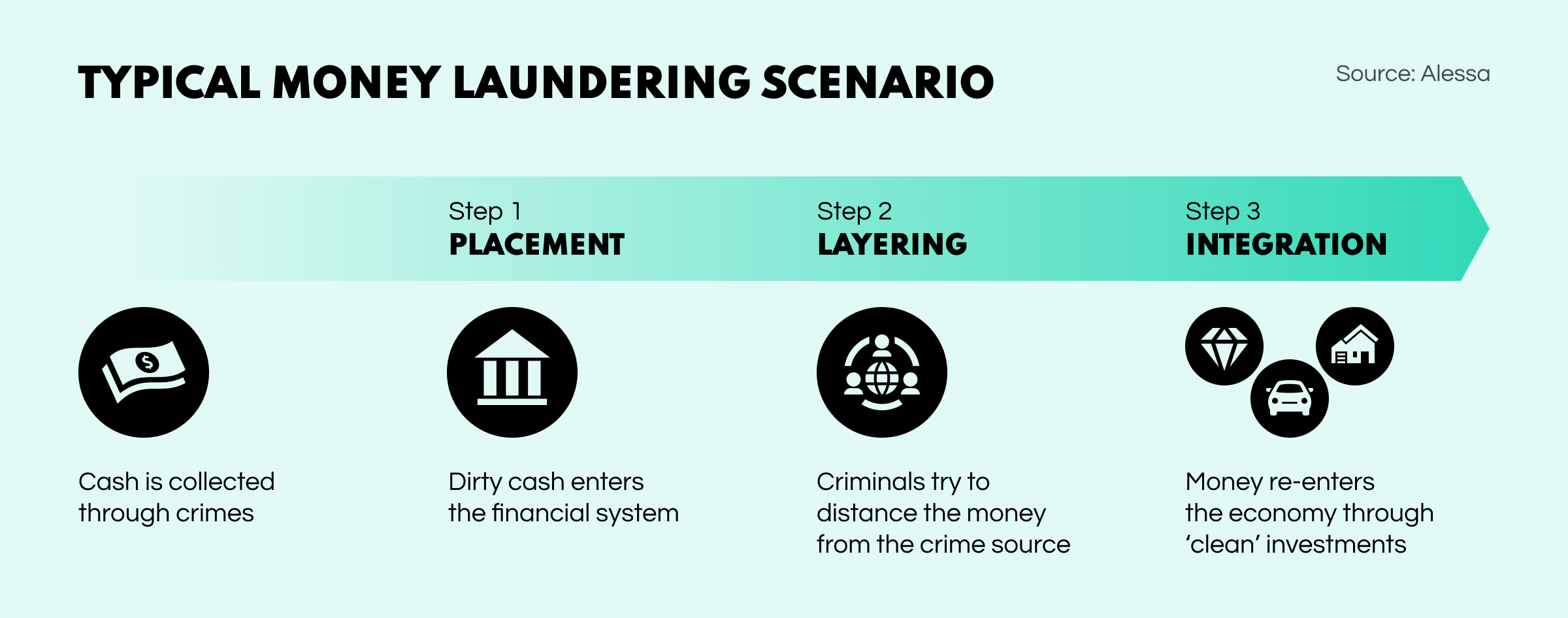
Anti-Money Laundering (AML). The second expression refers to the set of rules and regulations attempting to detect money laundering. Financial institutions, such as insurance firms, investment companies, or banks, have the responsibility to be vigilant for any shady dealings. For instance, if someone suddenly deposits a large amount of cash without a valid explanation, it raises a concern. The bank must report the transaction and investigate further to ensure the financial system remains safe.
Commonly AML measures are implemented before institutions establish relationships with clients. These processes include Know-Your-Customer (KYC) checks, thorough background investigations, and due diligence. Financial audits help evaluate whether a potential customer is involved in money laundering.
Official figures reveal an estimated $800M-$2T is laundered globally each year, accounting for 2-5% of the world's GDP. However, despite the staggering amount, reports indicate that 90% of money laundering cases go unnoticed, posing significant challenges to the integrity of financial systems. Yet, AML measures have an impact beyond organized crime, as they can be integral to countering wrongdoing in general.
According to the IC3, cybercrime losses surpassed $10B in 2022. But despite online scams being a growing problem, the stolen money still ends up in the banking system. This means that if AML systems were stronger, the attempts of fraudsters to legitimize their illegal gains from scams and other illicit activities could be easily identified, preventing the crime from progressing.
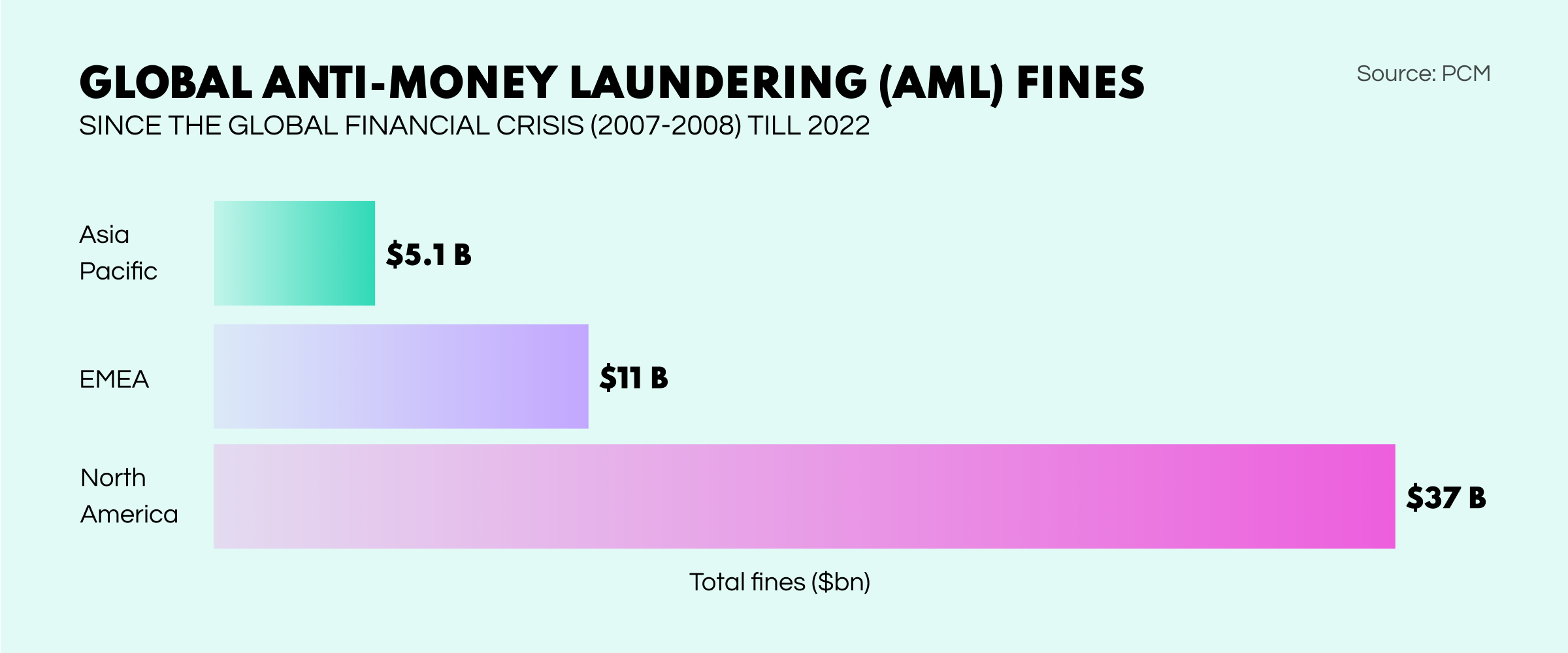
To ensure financial institutions follow anti-money laundering rules, regulators enforce strict penalties when firms fail to run proper checks. In 2022, organizations paid nearly $5B in fines globally. Thus, non-compliance payments have reached $56.1B since the 2007-2008 financial crisis. Such (sad) statistics indicate that the current incentives are not strong enough to deter money laundering. Indeed achieving compliance takes time. But it doesn't mean creating a more robust financial system is impossible.
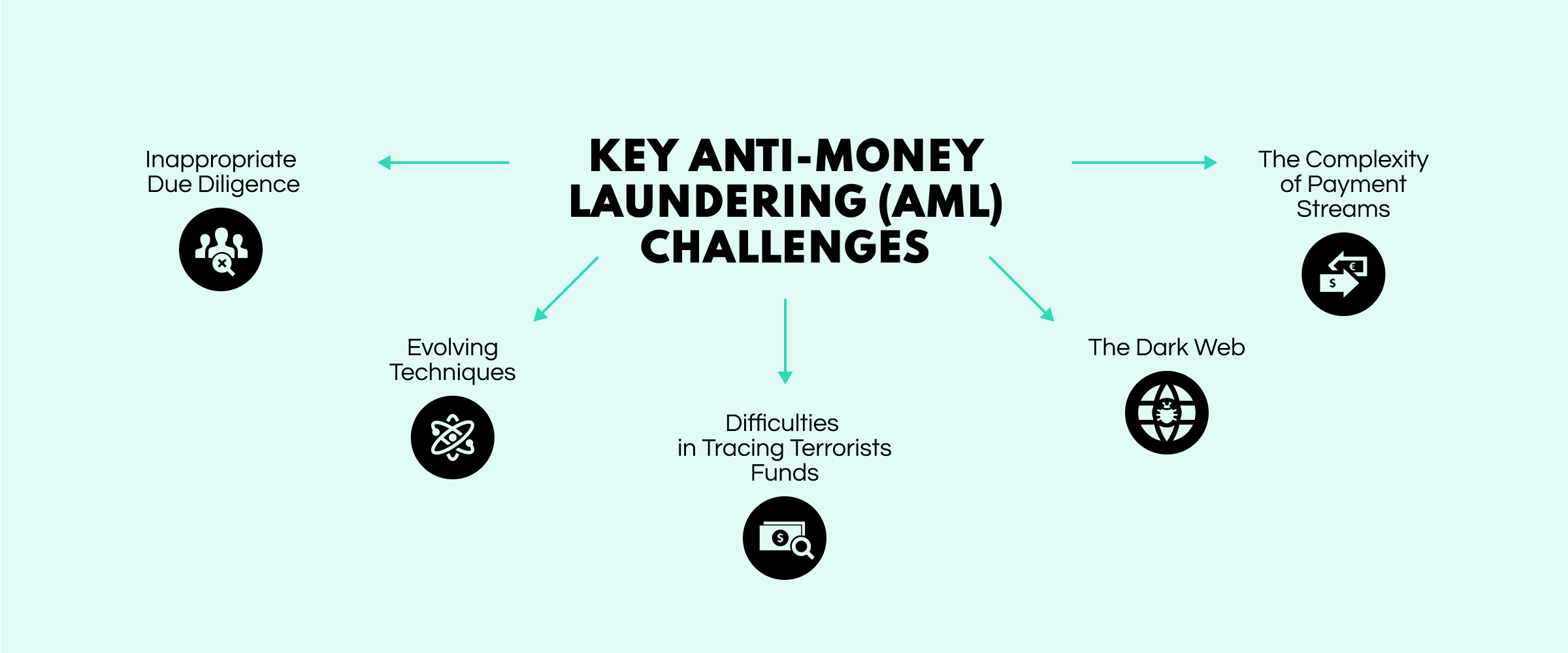
Understanding the importance of Anti-Money Laundering (AML) processes is crucial. However, implementing these measures can be challenging. Financial systems have many moving pieces, but if some parts weaken, it can disrupt the whole structure. Let's take a closer look at the main issues that impact the field of anti-money laundering.
In one of our earlier articles, we discussed the importance of customer screenings to stop money laundering. If financial institutions rush through their audits, they might end up accepting clients involved in money laundering. Such mistakes can lead to serious trouble like fines, legal problems, or damage to the reputation, resulting in unpredictable losses.
Case in point, the Estonian branch of the Danske Bank was fined $2B in 2022 by the US Department of Justice (DOJ). Court filings revealed that the institution allowed for laundering of $212B from high-risk individuals spread across various countries. According to the prosecutors, the AML program of the bank was insufficient to detect suspicious activity, clearly illustrating the massive impact of weak due diligence processes.
When a new technology arrives, malicious actors tend to be the first people to find a way to exploit it for personal gain. Criminals involved in money laundering are no exception. They constantly discover new ways to conceal their illegal actions, sometimes in the unlikeliest places, such as the video game Fortnite. The popular battle-royale game became a hotbed for money laundering, with fraudsters buying in-game currency with illicit gains and reselling the user profiles on auction sites to launder their cash.
And then we have Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs). These digital assets exploded in popularity around 2021 and have become a new tool to launder money. In fact, toward the end of 2021, NFT platforms received $1.4M from wallets associated with countries under sanctions. Such cases are possible as the platforms that sell non-fungible tokens don’t require a KYC check. Because of unclear regulations, malicious actors can hold more than one account and sell the token from one address to the other to drive up the price in a process called wash trading.
Terrorist groups employ various methods to conceal funds' source, movement, and purpose. Fundamentally, money laundering is closely linked to extremist activities. Such groups can transfer money across borders without arousing suspicion by exploiting charitable organizations, participating in trade-based money laundering (TBML), and more.
While organizations such as the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) are actively investigating and trying to strengthen AML regulations to stop terrorist funding, the process is an uphill battle at best. According to a statement by the FATF, despite the task force’s efforts, extremist organizations such as the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) and Al-Qaeda receive consistent funding through the donations of their supporters and illegal money laundering schemes, highlighting the crucial importance of effective regulations.
This shady part of the Internet presents a major challenge due to the anonymity it offers to its users. Transactions usually occur through secure channels and aliases, making it difficult for authorities and financial organizations to identify the individuals involved. However, because the Dark Web is not illegal to access and use, it is a bridge for many money laundering operations within the space.
A recent example was the news site DeepDotWeb, which published articles about the events surrounding the darknet. The website had mirrors on the Surface and Dark Web and published reviews and interviews on underground services. When the platform admins were apprehended, it was revealed that the site was laundering money for many of the marketplaces it was advertising. This was achieved by transferring digital currencies to other Bitcoin wallets and bank accounts and getting paid in bribes totaling $8.4M.
Digital finance has revolutionized how money is exchanged, leading to a surge in e-commerce popularity. However, along with these advancements, new challenges have emerged. Financial institutions have faced difficulties investigating modern payment methods, such as prepaid cards and cryptocurrencies. As the ease of moving money increases and regulations remain lenient, money laundering becomes a multiple-choice question with more than one correct answer for criminals.
A popular method of legitimizing illicit funds is crypto mixer services, which on a basic level, charge a fee to break up a transfer into thousands (sometimes millions) of smaller transactions to scramble the origins. One such platform was ChipMixer, which North Korean and Russian hackers extensively used to launder over $700M since it was founded in 2017. While authorities have taken the service down, similar operations such as TornadoCash are still active and successfully laundered $7B for malicious actors since 2019.
Despite the challenges in AML compliance, there is a light at the end of the tunnel. Open-source intelligence tools can help analysts enhance their capabilities, identify red flags on time, and streamline the investigation process. Let’s take a look at how.
Online traces are an inevitable part of the Internet, where everything a person leaves a mark that investigators can track. OSINT tools can identify connections to social media accounts, tagged geolocation data, and lists of friends and associates through names, email addresses, phone numbers, and other open data. These pieces of information can further allow investigators to create a detailed profile of a subject’s actions which can quickly reveal money laundering activity.
Criminals engaged in money laundering schemes often use messengers like Telegram due to its perceived anonymity. However, open-source intelligence solutions allow scanning the platform's content to gain deeper insights and enrich the scope of the investigation. This can be achieved through a search by specific keywords, an alias, phone number, or Telegram ID; detection of links to closed groups; analysis of administrators' activity; or access to deleted content. All gained data can significantly enrich investigations and help uncover money laundering schemes.
It doesn’t matter how complicated money transfers are; it is possible to track all financial transactions somehow. As such, open-source intelligence enables investigators to follow paper trails and account movements by cross-referencing public records, financial websites, and internal organizations' records. Furthermore, OSINT can become vital in identifying sketchy fund transfers and irregularities, visualizing key information that may reveal non-obvious connections between malicious accounts and individuals.
No amount of encryption can effectively hide criminal activities. Open-source intelligence solutions enable investigators to track money laundering schemes through the darknet by scanning data sources, underground marketplaces, and forums to gather actionable insights against malicious actors. Furthermore, it is possible to deanonymize hidden profiles by cross-referencing information from the Surface Web and darknet posts (even deleted ones) and conduct searches based on usernames and crypto wallet addresses, which creates opportunities to gain actionable insights.
Understanding how specific individuals are related to companies can become vital information in AML programs. OSINT allows investigators to visualize the organizational structure of companies by scanning corporate registries. In many cases, such insight can become extremely valuable because the open-source intelligence tools can deepen awareness by including sanctions databases in the research process and analyzing if any individual is a Politically Exposed Person (PEP). The comprehensive insight that OSINT offers can reveal any shadow ties a subject may have, significantly reducing money laundering risks.
Terrorist organizations usually spread their financial actions across multiple countries, allowing them to exploit regulatory weaknesses in AML systems. However, by collecting data from official sources such as financial records and registers, OSINT becomes highly valuable when investigating extremist groups’ assets. Such insight can play a pivotal role in dismantling terrorist money laundering schemes. In addition, open-source intelligence solutions can further enrich the data by conducting searches through social media and online forums, which can link suspects to known terror groups.
Even though blockchain technology offers a degree of transparency through publicly available ledgers, trying to navigate that data can become difficult. OSINT tools can bridge the gap and identify malicious crypto wallets by cross-referencing transactions and the connections between addresses. With advanced features such as decentralized group detection through common links and tracking money transfers across networks, financial crimes can be identified more reliably.
And that’s a wrap on our article about using OSINT in full-term anti-money laundering investigations. We hope you got valuable insights and learned how to use open-source intelligence to strengthen your current AML workflow. In the meantime, stay tuned for our next piece and keep on investigating!