OSINT: A New Force in Cyber Security


There was once a time when cyber security felt like an exclusive issue – something that needed to be taken seriously by banks, governmental bodies, or companies handling sensitive data, but not a major concern for the average enterprise. However, with IBM listing cyber security failure as one of most formidable problems facing the world today, that’s no longer tenable.
Breach costs are ballooning and it seems that no perimeter is air tight or immune to cyber threats. US federal databases were recently hacked into via software used by the government to track cattle. Meanwhile the mighty hardware corporation Nvidia has just been held to ransom by cryptocurrency enthusiasts demanding the removal of inbuilt hardware restrictions that inhibit the mining potential of their GPUs.
Make no mistake, data breaches represent a significant threat which has spiraled out of all control in the last decade. Yet OSINT techniques and tools may just provide the resistance we need. This article will go into what the current situation is, how we got here, and how OSINT cyber security technologies are being leveraged to combat the problem across a number of sectors.
There may have been some complacency here. Despite the statistics, the prevailing attitude seems to have been one of vague denial: ‘It probably won’t happen to us.’ Well, that simply doesn’t fly anymore. The unsettling truth is that, at some point or another, it probably will happen to you. As it stands, 64% of companies worldwide have experienced a cyber attack, and that figure is on the rise.
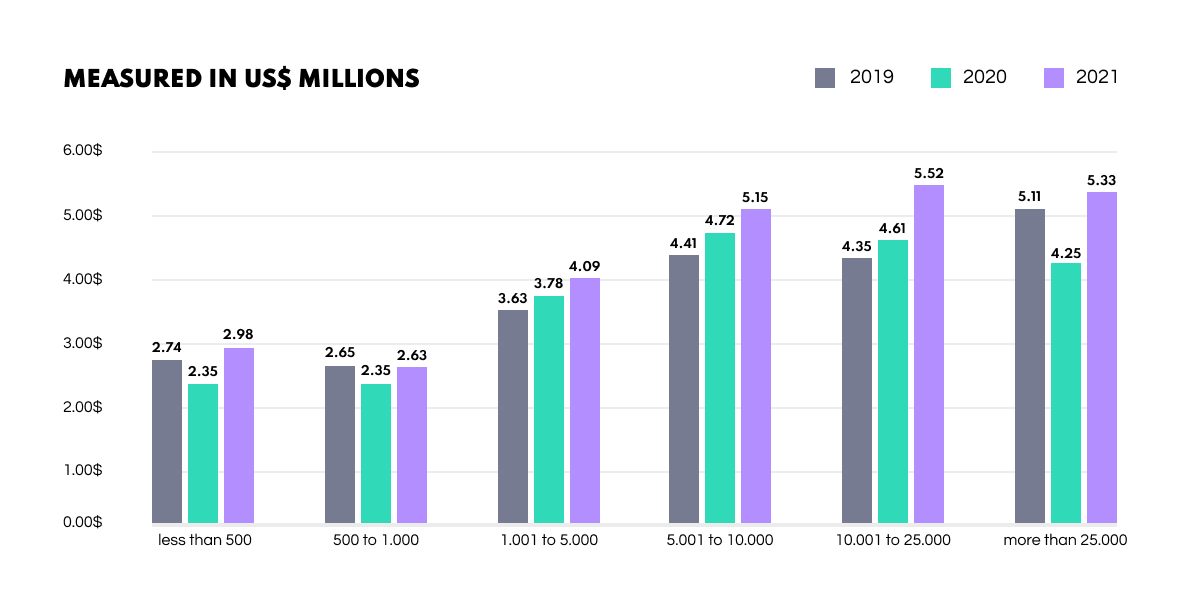
For further context, organizations are now 30% more likely to undergo a data breach than they were in 2014. And it’s not just the likelihood which matters, it’s also the expense. In the last year alone, the average cost of a data breach rose by 10% to $4.24 million. And you might say: ‘Well, that’s mainly just large companies.’ Nope.
While vast corporations do experience the most severe costs overall, organizations with less than 500 employees are now paying out more than those with a workforce between 500 and 1000 people. Never before has the cyber security industry been in such high demand across the board.
With the cyber security issue reaching such troubling proportions, a natural question is: how did this situation move from the backburner to one of the foremost international problems? Well, there are a number of factors, but some are more prominent than others.
It really has been a thorn in our side. Of course, this is about the widespread migration to remote work – a situation that was forced on most organizations as a natural measure in response to the pandemic. This has unfortunately had quite serious ramifications for data security, as companies have been far less able to retain a secure IT perimeter.
Instead of secure networks established and monitored by IT teams, organizations now deal with a jumble of different routers and networks which each remote worker has set up themselves. Furthermore, collaboration tools and conferencing platforms represent another layer of vulnerability, with even established companies such as Microsoft and Zoom struggling to patch up all the bugs that allow opportunities for infiltration.
Then there’s the adoption of home equipment. According to a study conducted by Kaspersky, 80% of remote workers accessed their company infrastructure via their personal computers even though the majority had been provided with a company alternative. With home internet usage often including torrent downloads and content streaming from unreliable sites, the increased susceptibilities to cyber threats are clear.
While this is hardly a new cause of data breaches, it has now firmly established itself as the most common. Part of the reason for this is that it is practically impossible to eliminate, but also because it lurks behind all four breach causes of the apocalypse: business email compromise, credential compromise, social engineering, and phishing.
Credential compromise can stem from anything between a cloud misconfiguration to a careless social media post from a sensitive workplace. Meanwhile, phishing and social engineering axiomatically depend upon human error. This could be user misdirection through seemingly legitimate emails or more interpersonal schemes such as a phone call from a bogus IT guy, requesting some verification…
For cybercriminals, they are unquestionably the payment method of choice. For one thing, the perceived anonymity of cryptos provides the cloaking needed for transacting an illicit deal without being traced. Secondly, the rise of crypto mixers enable cybercriminals to legitimize their ill-gotten gains in a straightforward laundering process.
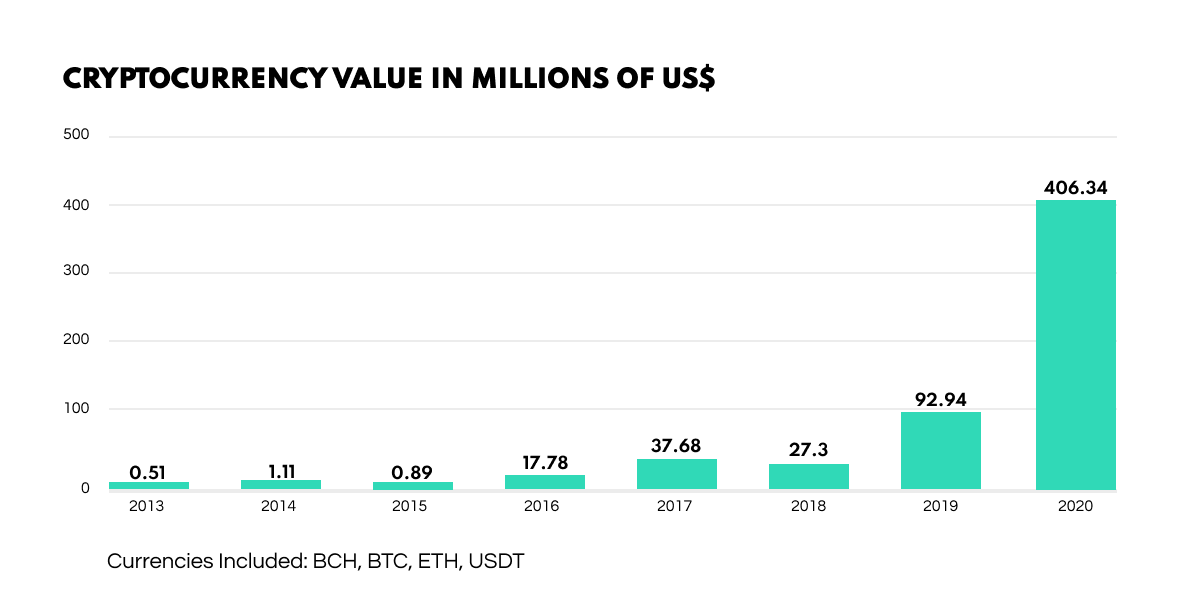
Figures on ransomware payouts via cryptocurrencies illustrate how blockchains are mobilizing opportunities for cyber threat actors. According to a Chainalysis report, the total cryptocurrency value received by ransomware addresses more than quadrupled between 2019 and 2020, jumping from approximately $93 million to a staggering $406 million.
So, where do OSINT tools enter the cyber security landscape?
A cornerstone of cyber security, threat intelligence broadly refers to the methods and processes by which an organization identifies vulnerabilities to inform counter-breach measures. Cyber threat susceptibilities come in a variety of forms and emerge from all levels of an organization, from premises and facilities, through personnel and corporate culture, to the overall public perception.
In other words, the more detailed and expansive a threat actor’s understanding of an organization is, the more breach opportunities there are on the table. Today, OSINT cyber security tools and techniques are extensively used in penetration testing to help infosec professionals determine weaknesses by considering their organization in the way a threat actor would.
Let’s take phishing as a more specific example. Knowledge of company facilities such as IoT items as well as software and hardware can be priceless to the hacker. Someone planning a phishing scam can use this information to engineer an email that looks like an utterly authentic missive from a software developer who the company has a contract with. This type of bait would clearly be more effective than an ill-focused piece of spam.
Using OSINT tools, cyber security teams can gain a detailed picture of the organization’s informational vulnerabilities on both a corporate and individual level. The automated search methods of open-source intelligence tools significantly help pen testers in flagging up a wide range of security gaps from obvious disclosures to more obscure, inadvertent risks like a single employee not being guarded enough on social media.
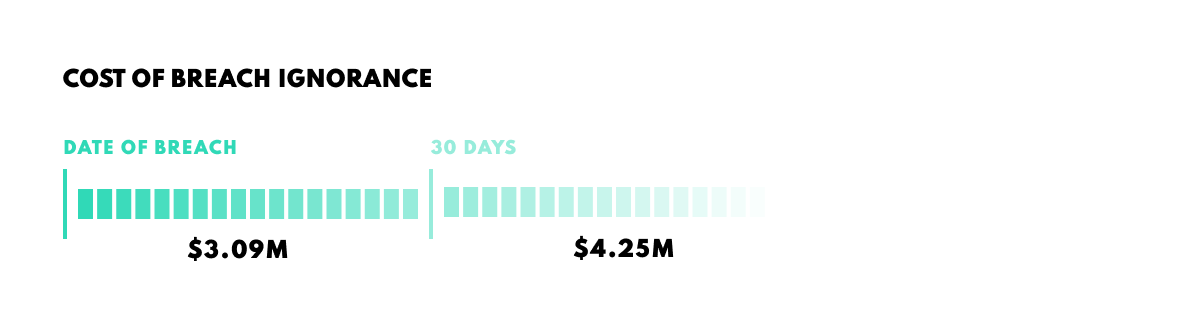
Returning again to IBM’s data breach report for 2021, there is a principle catalyst behind the spiraling financial costs of data leaks. That catalyst is time. In particular, response time. According to the report, the average breach lifecycle is 279 days – 206 days for the leak to be identified, then a further 73 days for it to be contained.
Lengthy as these response times are, their central significance lies in the costs that accrue as the time ticks away. Breach lifecycles under 200 days cost, on average, $1.26 million less than those which exceed 200 days – the difference between $3.61 million and $4.87 million. Time is certainly of the essence.
How OSINT solutions help. Indications of data leaks inevitably surface online, but are effectively lost in the ocean of open data. Searching manually for these signs would be a thankless and fruitless task. But the search methods available through OSINT cyber security software, can constantly monitor the Surface, Deep and Dark Web for these needles in the haystack.
By returning all possible symptoms of a leak, cyber security professionals can investigate these points further, so that if a leak has indeed occurred, the organization knows about it immediately. Machine learning and other progressive technologies contribute to the efficacy of OSINT cyber security tools, which are saving millions of dollars for organizations around the globe.
Again, the perceived cloaking provided by cryptocurrencies makes it an attractive option for suspect transactions. Yet, in actual fact, the anonymity threat actors depend on is really not as effective as is widely believed. There are ways to trace what at first glance may seem untraceable, and OSINT cyber security tools play a major role in this.
How OSINT solutions help. Cryptocurrencies are open data sources and can be explored like any other. Using open-source intelligence tools to scrutinize the blockchains of Bitcoin, Etherium and other cryptos, transactions can be traced to wallets. These, in turn, can be connected to other identifiers that may appear on the Dark or even Surface Web – and it’s goodbye anonymity.
Even cryptocurrency mixers – the go-to laundering method for many cybercriminals – are not totally resistant to the unpacking potential that OSINT cyber security technologies provide. This means that finances which are suspect can actually be identified as such, and a ransomware payout can remain a discredited asset.
In the current climate, there is not just a need, but an urgent imperative for the application of OSINT in cyber security. With the widespread adoption of open-source intelligence tools and techniques, the challenges of cyber security will hopefully become more and more manageable, and companies will be able to each play their part in mitigating a problem which has become such a worldwide concern.