OSINT and Fraud Prevention: from Data to Defense

Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the world has undergone significant transformations. Remote work has become the new normal, online shopping has skyrocketed in popularity, and fraudulent activities have taken on a new level of sophistication. AI-generated fraud, in particular, is posing the most significant threat. So much so that according to a survey conducted by Regula Forensics, scammers targeted 46% of global organizations with some form of generative identity fraud in 2022.
In this article, we’re looking at the importance of using OSINT in fraud prevention. We’re going over the different types of scams, the global climate surrounding them, and how open-source intelligence can provide a way forward. With scams costing users millions in damages, see how it’s possible to prevent such losses through the application of open-source intelligence.
Fraud (or scams) involves deceiving others for personal gain. These crimes can manifest in various ways, and it's crucial to understand the differences. While the following list is not exhaustive, let's delve into some prominent examples of scams to better understand how they operate and the significant financial losses they inflict on victims.
Identity Fraud. A criminal steals someone's personal information, such as a social security number or bank details. Then, the threat actor impersonates the victim to open credit card accounts, make unauthorized purchases in their name, or contact family members and ask for money.
Brand Impersonation Fraud. This case is closely related to identity theft but primarily concerns businesses. Brand impersonation fraud occurs when a criminal creates a fake website, email, or social media account resembling a well-known trademark to trick people into sharing personal information or making fraudulent payments.
Investment Fraud. With the rise of cryptocurrencies, these scams have grown in popularity. A malicious actor promotes a low-risk, high-reward investment project. When victims give their money to the scammer, the lucrative opportunity turns out to be a pig butchering scheme. The fraudster receives the victim’s funds and then disappears.
E-commerce Fraud. While these scams occur in many different ways, the core idea remains the same. A threat actor creates a fake online store, advertising popular items at very low prices. When customers make their purchases, they never receive the products, as the store functions solely to collect payments and disappear.
Advance Fee Fraud. The victim receives an email from someone claiming to be a foreign official (frequently a prince) who needs assistance transferring a large sum of money out of their country. The victims must pay a small upfront fee with the promise of receiving several million. But of course, after paying, they never hear from the scammer again, or even worse, the malicious actor gets access to the entire bank account.
Romance Scam. Documentaries like 'The Tinder Swindler' brought this type of fraud into daily conversations. The working principle is simple: a threat actor develops an online relationship with someone (which can last years), gaining their trust and affection before requesting money for a phony emergency or travel expenses and disappearing after receiving the funds.
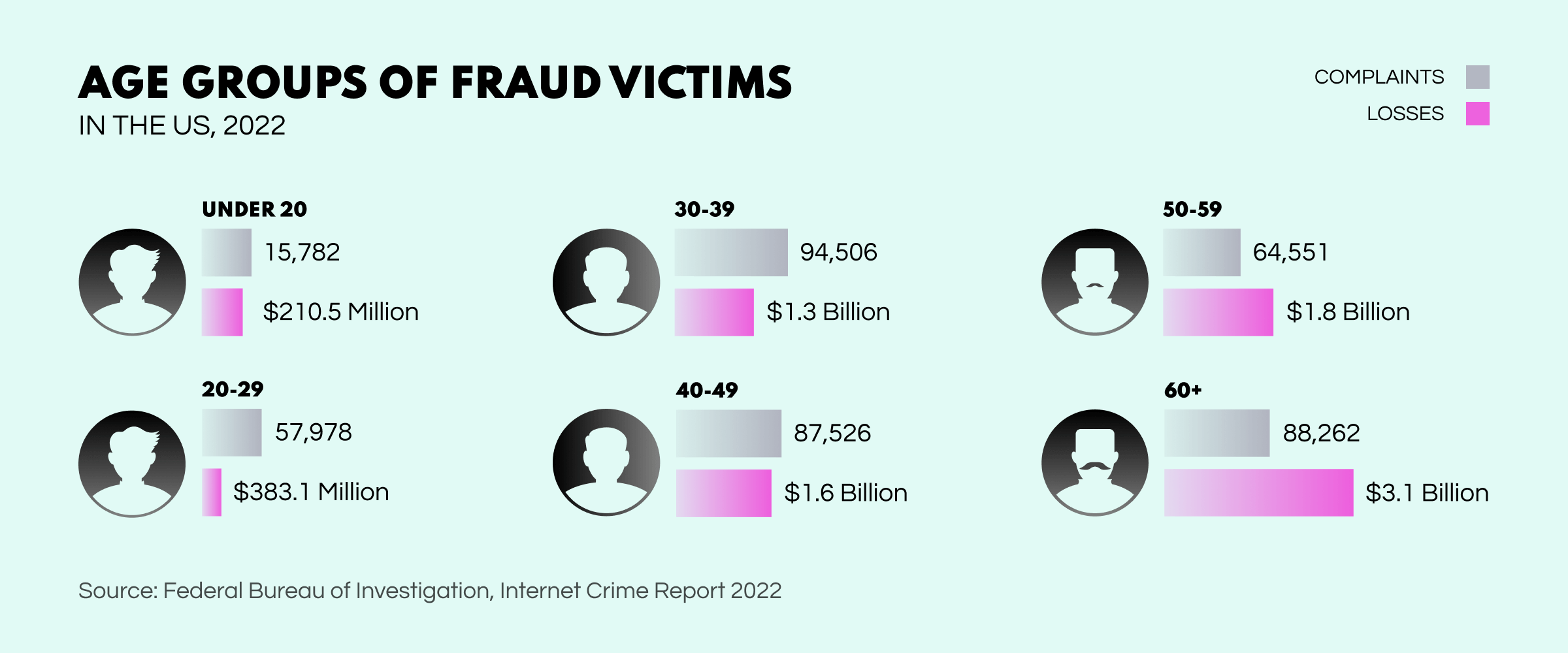
Elder Fraud. The scammer targets a senior person by posing as a government official, charity worker, or family member and tricking them into providing personal information or transferring money under false pretenses, exploiting their vulnerability. While age does play a role in determining scam victims, criminals target all demographics. However, elder fraud shows a sharp increase in 2022, with losses increasing by 84% since 2021.
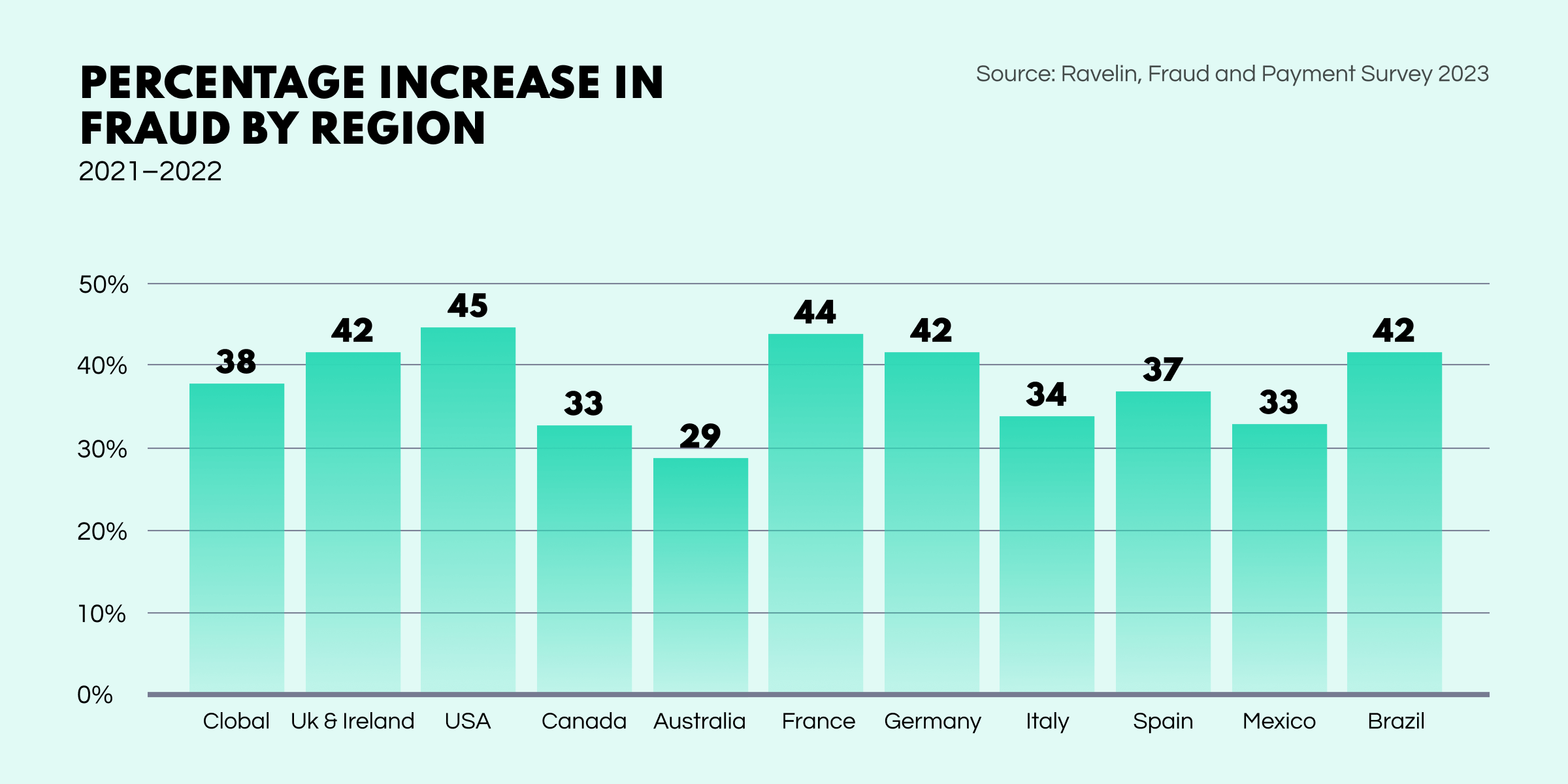
Scams have become a pervasive problem worldwide, with severe financial consequences. In 2022, scam losses surpassed $8.8B in the US alone. Juniper Research predicts that global online payment losses will reach an astonishing $343B between 2023-2027. In fact, according to Ravelin’s survey, fraud rates are up by 38% in 2022, and technological innovations are resulting in new forms of scams.
One of the major contributors to the evolving landscape of fraud is the emergence of AI tools like ChatGPT. These advancements have given rise to new types of criminal activities, such as AI-driven voice impersonation cons. Malicious actors exploit these schemes by targeting families, posing as their distressed children and requesting money. The impact of such scams is evident, with the FTC reporting over $11M in losses from 5.1k fraudulent phone calls in 2022.
The COVID-19 pandemic brought about significant changes in the world of fraud. As people turned to online shopping due to lockdowns and restrictions, e-commerce witnessed a remarkable surge in popularity. Exploiting this shift, malicious actors redirected their attention to the digital domain. Reports from the FTC indicate that fraud losses in 2021 skyrocketed to $5.8B, marking a staggering 70% increase compared to the previous year. Such figures emphasize the urgent need for effective fraud prevention measures in the face of evolving criminal tactics.
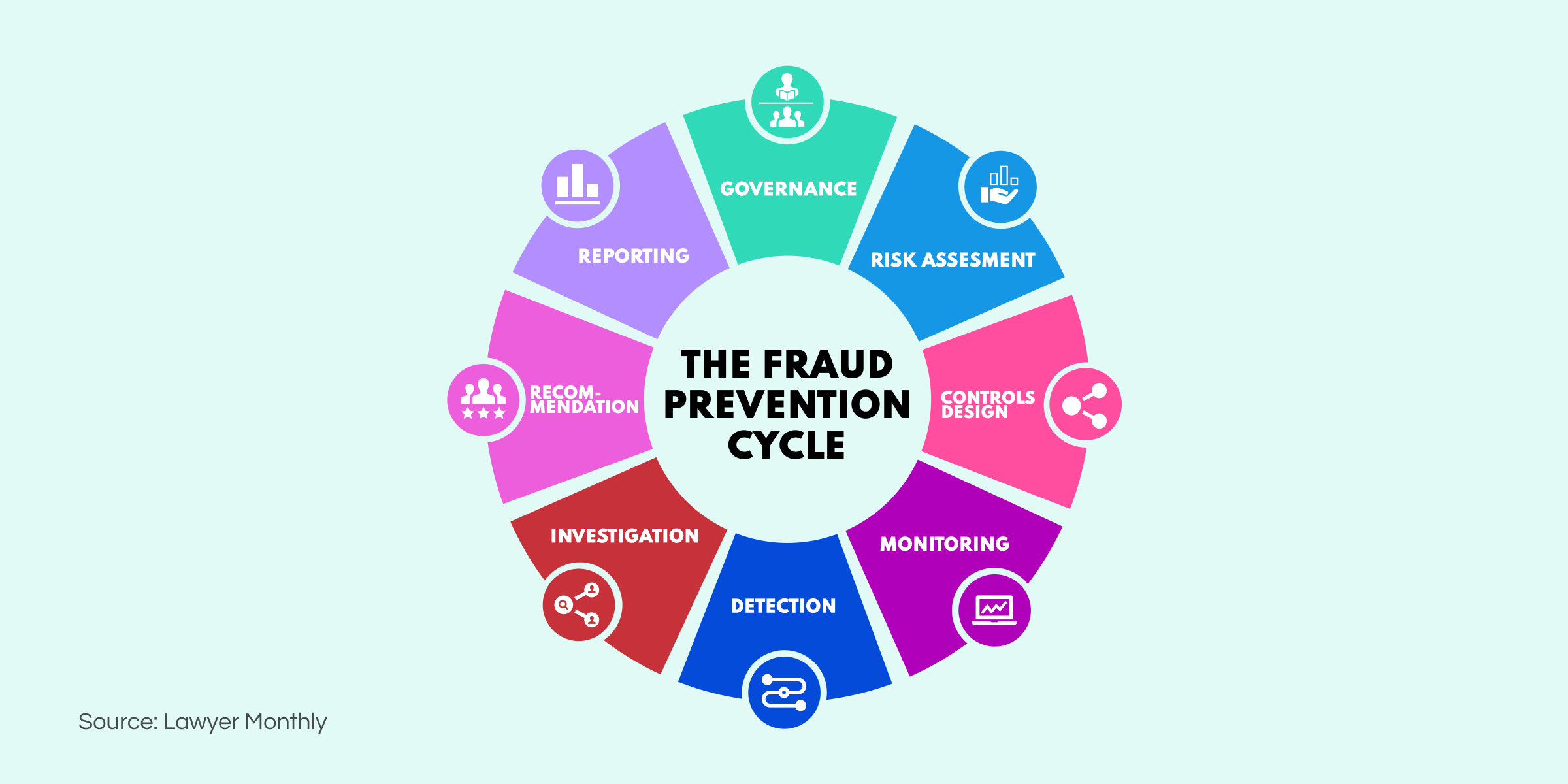
Open-source intelligence plays a prominent role in the fraud prevention cycle by providing specialists with robust tools to handle the Monitoring, Detection, and Investigation stages effectively. OSINT allows investigators to extract valuable insights to identify scammers and stop massive financial losses. The following are the primary ways open-source intelligence supports the fight against fraud:
And that’s the conclusion of our article on OSINT in fraud prevention! We hope you found valuable insights and gained a deeper understanding of how open-source intelligence techniques play a crucial role in combating scams. To stay informed and ahead of the curve, be sure to regularly visit our blog for updates and insightful content on the world of OSINT.